The Hidden Cost of Sleepless Nights
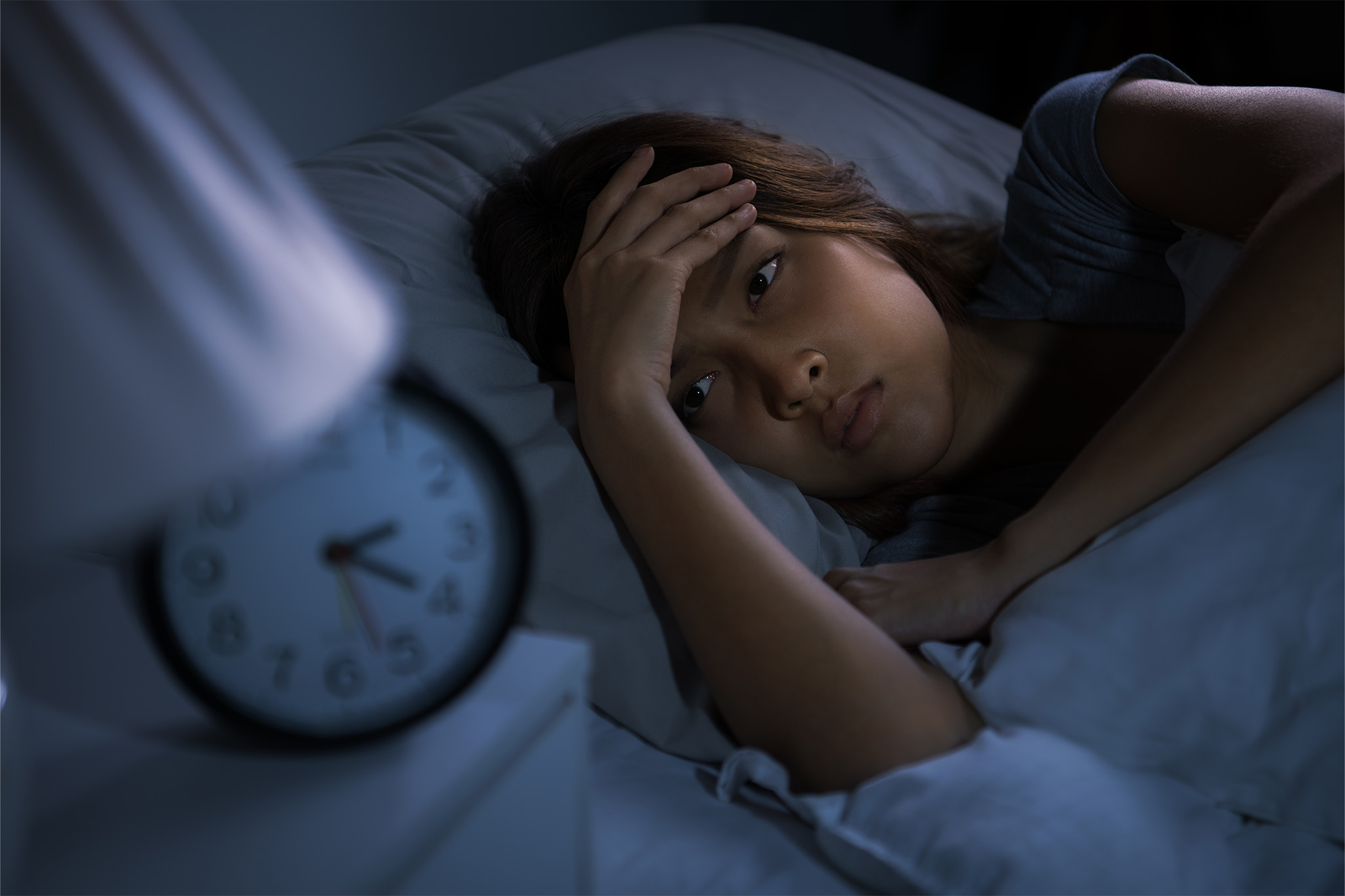
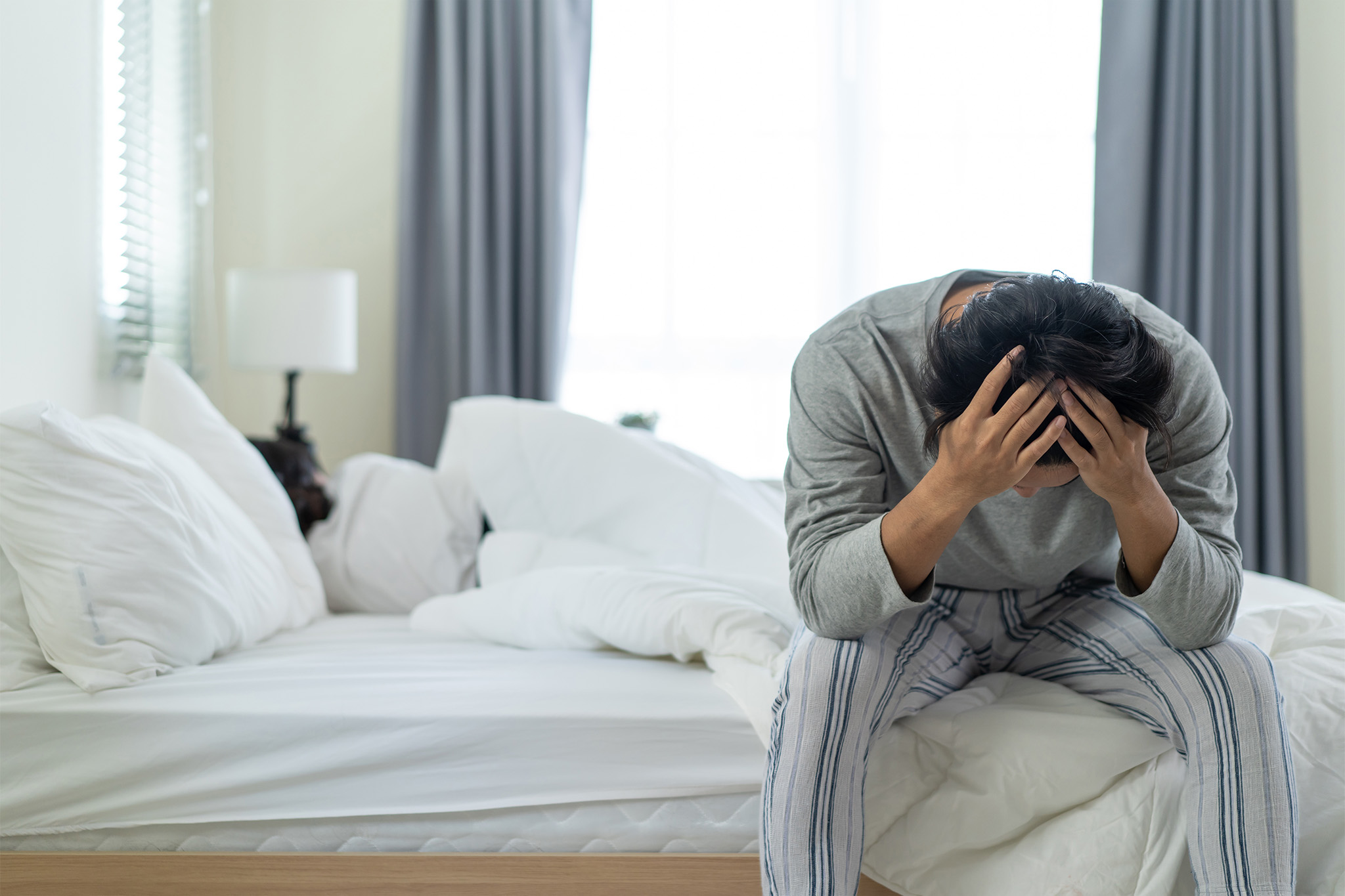
Tossing and turning at night is more than just frustrating. Chronic insomnia affects about 1 in 3 adults at some point in life, and it doesn’t just make you tired — it disrupts nearly every system in your body.
Sleep is when your brain, hormones, and organs reset. Without enough of it, the effects ripple into your metabolism, mood, and even how fast you age.
Causes of Insomnia
Insomnia often has more than one cause. Common triggers include:
- Stress and anxiety (the most common culprit)
- Poor sleep habits (irregular bedtime, late-night screen use, caffeine)
- Medical conditions (pain, thyroid imbalance, sleep apnea, reflux)
- Medications or stimulants
- Environmental factors (noise, light, uncomfortable room)
How Poor Sleep Alters Your Hormones
A single bad night affects your focus. Weeks or months of insomnia affect your hormones:
- Cortisol (stress hormone): Stays elevated, making you anxious and wired.
- Insulin: Sensitivity decreases, increasing risk of weight gain and diabetes.
- Leptin & Ghrelin: Appetite-regulating hormones are disrupted, leading to food cravings.
- Melatonin: Natural rhythm is blunted, making it even harder to fall asleep.
- Growth hormone: Released mostly at night; poor sleep reduces repair and accelerates aging.
In other words: sleep isn’t optional. It’s the foundation of hormonal balance and healthy aging.

The Gold Standard: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
The best evidence-based treatment for chronic insomnia is not a pill, but Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I).
- Helps break the cycle of anxiety around sleep
- Retrains your brain and body to associate bed with rest, not frustration
- Involves structured techniques (sleep restriction, stimulus control, relaxation methods)
- Long-term success is higher than with sleep medications
What You Can Do Tonight
Simple but powerful steps make a difference:
- Set a routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same time daily.
- Control light: Dim lights 1–2 hours before bed, avoid screens, and keep the bedroom dark.
- Cool and quiet: Keep your bedroom slightly cool — ideally 18–20 °C — which supports your body’s natural drop in temperature for restful sleep. Make sure the space is dark and quiet.
- Wind down: Use relaxation techniques — breathing, journaling, or meditation.
- Limit stimulants: No caffeine after midday, no alcohol close to bedtime.
Helpful Adjuncts
For some, supportive strategies help improve sleep quality:
- Supplements: Melatonin, magnesium, or L-theanine (doctor-guided).
- Massage therapy: Promotes relaxation and lowers cortisol.
- Aromatherapy: Lavender and chamomile oils can aid calmness.
- Tryptophan-rich foods: Turkey, eggs, bananas, and nuts provide building blocks for serotonin and melatonin.

PrimeCare’s Approach
Everyone’s insomnia has a different root cause. At PrimeCare, we combine:
- Medical evaluation (to rule out thyroid issues, sleep apnea, or other underlying causes)
- CBT-I guidance as the first-line, evidence-based therapy
- Lifestyle and environment coaching for better sleep hygiene
- Personalized options like supplements, IV support, or stress-reduction therapies
Your Sleep, Your Health
Poor sleep doesn’t just leave you tired — it accelerates aging, disrupts hormones, and affects every aspect of life. The good news: insomnia is treatable, and better nights mean better health.
Book a consultation with our doctors at PrimeCare. Together, we’ll create a personalized sleep plan that restores your rest — and your vitality.